
We propose a new algorithm for the reliable detection and localization of video copy-move forgeries. Discovering well crafted video copy-moves may be very difficult, especially when some uniform background is copied to occlude foreground objects. To reliably detect both additive and occlusive copymoves we use a dense-field approach, with invariant features that guarantee robustness to several post-processing operations. To limit complexity, a suitable video-oriented version of PatchMatch is used, with a multiresolution search strategy, and a focus on volumes of interest. Performance assessment relies on a new dataset, designed ad hoc, with realistic copy-moves and a wide variety of challenging situations. Experimental results show the proposed method to detect and localize video copy-moves with good accuracy even in adverse conditions. The software and dataset are available online for the interested researchers.
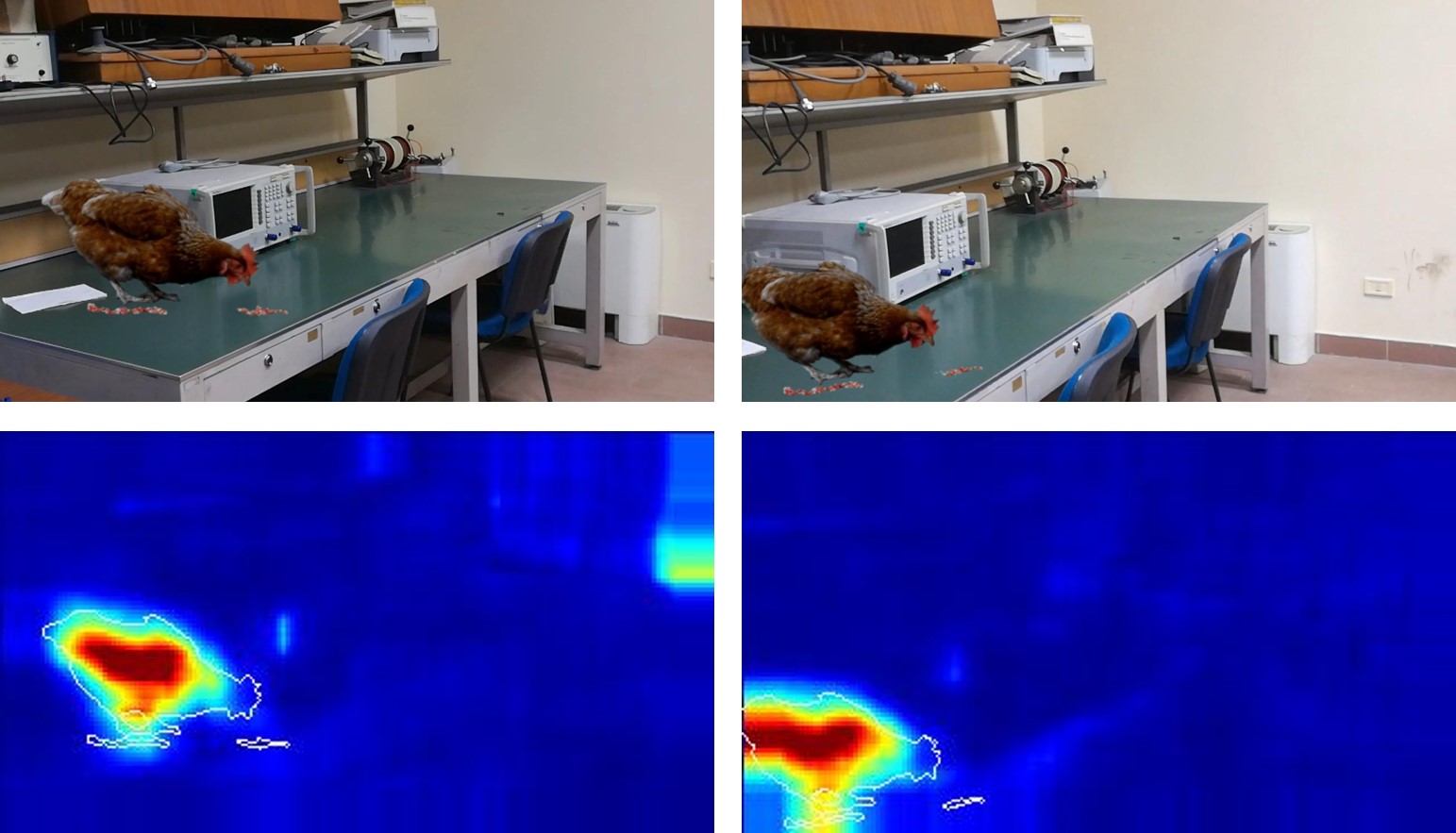
Video forgery detection is becoming an important issue in recent years, because modern editing software provide powerful and easy-to-use tools to manipulate videos. In this paper we propose to perform detection by means of deep learning, with an architecture based on autoencoders and recurrent neural networks. A training phase on a few pristine frames allows the autoencoder to learn an intrinsic model of the source. Then, forged material is singled out as anomalous, as it does not fit the learned model, and is encoded with a large reconstruction error. Recursive networks, implemented with the long short-term memory model, are used to exploit temporal dependencies. Preliminary results on forged videos show the potential of this approach.